Penelitian
Pengertian
Publikasi ilmiah adalah salah satu komponen penting dalam pendidikan tinggi. Dosen dan mahasiswa khususnya di tingkat doktoral sebagai peneliti dituntut untuk memiliki publikasi di jurnal internasional sebagai salah satu hasil dari penelitian yang telah dilakukan. Tidak hanya sembarang jurnal, kita dituntut mempublikasi hasil penelitian di jurnal terindeks, termasuk di Program Studi Doktor FK-KMK UGM mensyaratkan bagi mahasiswa doktoral untuk publikasi jurnal minimum pada Quartile 3 (Q3).
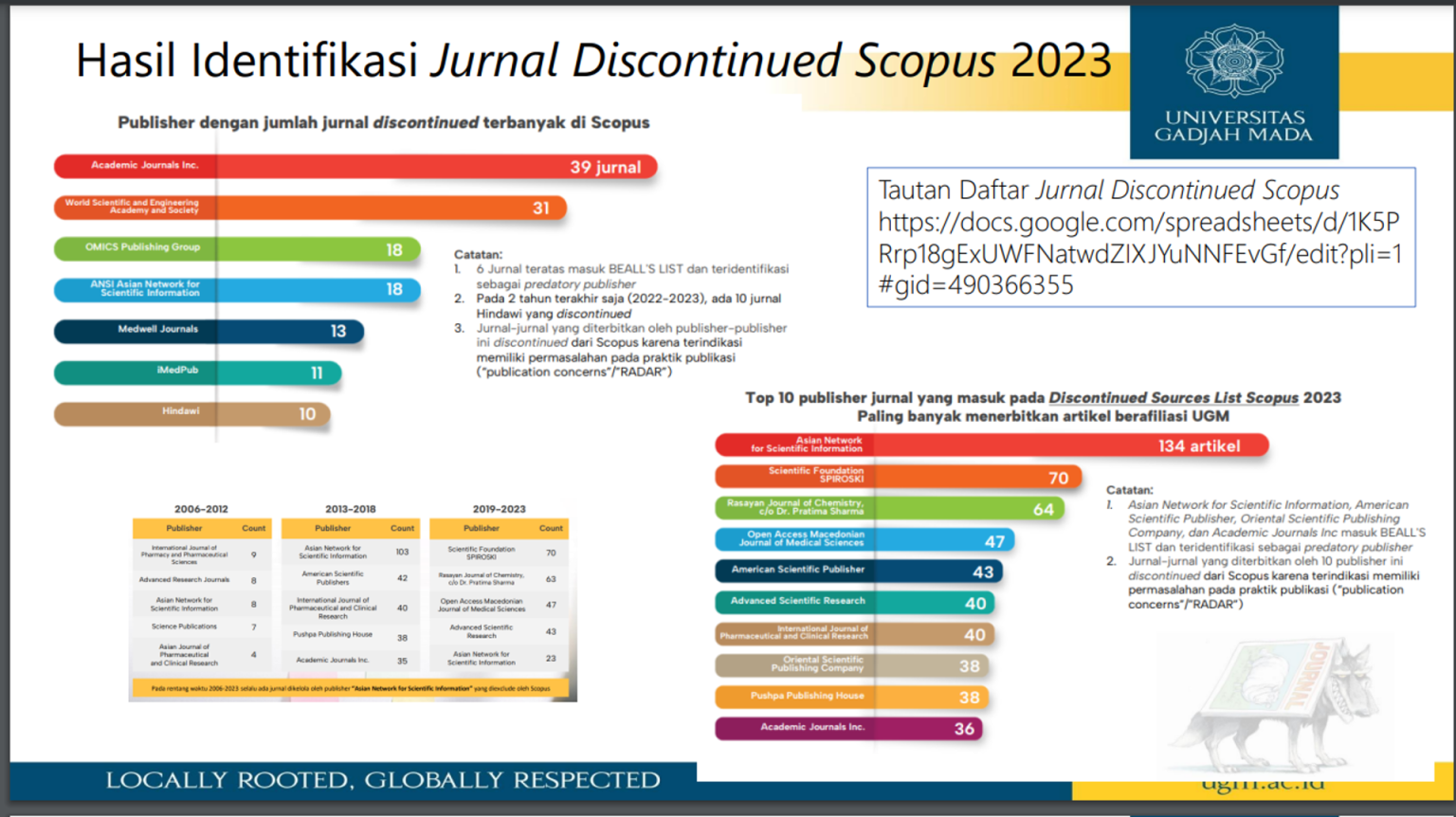
Saat ini ribuan jurnal diterbitkan di seluruh dunia. Namun, tidak sedikit jurnal-jurnal predator yang menawarkan proses submisi yang mudah dan cepat namun tidak bisa dipertanggungjawabkan kualitasnya. Hal ini perlu diwaspadai agar artikel dapat dipublikasikan di jurnal terindeks dan terjamin kualitasnya.
Kementerian Pendidikan dan Kebudayaan melalui Dikti telah mengidentifikasi jurnal-jurnal yang harus dihindari sebab dipertanyakan kredibilitasnya. Daftar dapat diakses melalui tautan berikut: Link
Tautan daftar lengkap Discontinued Sources List Scopus Edisi Agustus 2023: Link
Pemilihan jurnal memerlukan pertimbangan dari aspek kualitas jurnal. Bagi mahasiswa yang submit manuskrip ke jurnal yang diskontinyu Scopus setelah bulan Oktober 2023 dan manuskripnya kemudian accepted atau terpublikasi, maka manuskrip tersebut tidak dapat digunakan sebagai syarat untuk ujian tertutup.
Publikasi Mahasiswa dan Alumni Prodi Doktor FKKMK UGM

Evaluation of crystal violet decolorization assay and resazurin microplate assay for antimycobacterial screening
Maya Dian Rakhmawatie, Tri Wibawa, Puspita Lisdiyanti, Woro Rukmi Pratiwi, Mustofa
Abstract
The main obstacle in antimycobacterial discovery is the extremely slow growth rates of pathogenic mycobacteria that lead to the long incubation times needed in antimycobacterial screening. Some in vitro testings has been developed and are currently available for antimycobacterial screening. The aim of the study was to compare Resazurin Microplate Assay (REMA) and Crystal Violet Decolorization Assay (CVDA) for testing mycobacteria susceptibility to isoniazid and rifampicin as well as for antimycobacterial screening of natural products (NP). Mycobacterium tuberculosis strain H37Rv and Mycobacterium smegmatis strain mc2 155 were used as tested mycobacteria. Serial two-fold dilutions from 0.0625 to 1.0 μg/mL for the isoniazid and rifampicin and from 6.25 to 100.0 μg/mL for the NP A and B were prepared. Tested mycobacteria were then incubated with tested drugs or NPs in each growth medium at 37 °C for 7 days for M. tuberculosis and 3 days for M. smegmatis. MIC values against M. tuberculosis were interpreted 24–48 h after adding resazurin or at least 72 h after adding crystal violet, whereas MIC values against M. smegmatis were interpreted 1 h after adding resazurin or 24 h after adding crystal violet. The MIC values against M. tuberculosis interpreted by REMA were 0.0625, 0.0625, 6.25, and >100 μg/mL for rifampicin, isoniazid, NP A, and NP B, respectively, and those interpreted by CVDA were 0.0625, 0.0625, 6.25, and >100 μg/mL for rifampicin, isoniazid, NP A, and NP B, respectively. Moreover, the MIC values against M. smegmatis interpreted by REMA were 0.0625, >1, 6.25, and 100 μg/mL for rifampicin, isoniazid, NP A, and NP B, respectively, and those interpreted by CVDA were 0.125, >1, 6.25, and >100 μg/mL for rifampicin, isoniazid, NP A, NP B respectively. In conclusion, REMA is faster and easier than CVDA to interpret MIC values, however CVDA produces higher MIC values than REMA for rifampicin and NP B in M. smegmatis susceptibility testing. Therefore, REMA and CVDA can be used for antimycobacterial screening.

The effects of docetaxel and/or captopril in expression of TGF-β1, MMP-1, CTGF, and PAI-1 as markers of anterior urethral stricture in an animal model
Wikan Kurniawan, Marsetyawan Heparis Nur Ekandaru Soesatyo, Teguh Aryandono
Background:
Treatment of urethral trauma is currently done after urethral stricture occurs. Stricture therapy after occurrence gives unsatisfactory success rates. Several genes, such as transforming growth factor beta 1 (TGF-β1), matrix metalloproteinase 1 (MMP-1), connective tissue growth factor (CTGF), and plasminogen activator inhibitor 1 (PAI-1), have a proven role in urethral stricture development. The purpose of this study was to assess the effect docetaxel and/or captopril on the RNA expression of those genes.
Methods:
The subjects of this research were 26 male New Zealand rabbits aged 230 ± 20 days weighing 4–5 kg that underwent urethral rupture by endoscopic resection under anesthetized conditions. Subjects were divided into five groups; control, stricture, captopril (captopril 0.05 mg/rabbit/day), docetaxel (docetaxel 0.1 mg/rabbit/day), and docetaxel-captopril (docetaxel 0.1 mg/rabbit/day and captopril 0.05 mg/rabbit/day). Each group consisted of 4–6 rabbits. Each rabbit received a water-soluble transurethral gel containing drug according to its group for 28 days. After the treatment period, rabbits were sacrificed with 200 mg Pentothal, and the corpus spongiosum was then prepared for real-time PCR examination.
Results:
TGF-β1 RNA expression in the stricture group was statistically different from that in the control, docetaxel and docetaxel-captopril groups (p = 0.016; p = 0.016; p = 0.004). The stricture group did not exhibit any statistical difference from the captopril group (p = 0.190). The control group did not show any statistically difference from the captopril, docetaxel, and docetaxel-captopril groups (p = 0.114; p = 0.190; p = 1.000). Docetaxel-captopril suppresses expression of TGF-β1 RNA most significantly. MMP-1 RNA expression showed no significant differences among groups (p = 0.827). The docetaxel group and stricture group pair was most significant (p = 0.247), compared with other pairs of stricture groups in MMP-1 RNA expression. CTGF RNA expression in the stricture group was statistically different from that of control, captopril, docetaxel, and docetaxel-captopril groups (p = 0.003; p = 0.019; p = 0.005; p = 0.005). The control group did not exhibit any statistically difference from the captopril, docetaxel, and docetaxel-captopril groups (p = 0.408; p = 0.709; p = 0.695). There was no statistical difference among treatment groups. Docetaxel and docetaxel-captopril groups suppress the most significant expression of CTGF RNA expression.
PAI-1 RNA expression in the stricture group differed statistically significantly from the control and docetaxel groups (p = 0.044; p = 0.016). The stricture group did not show any statistically significant difference from the captopril and docetaxel-captopril groups (p = 0.763; p = 0.086). The control group did not exhibit any statistical difference with any of the treatment groups (p = 0.101; p = 0.637; p = 0.669).
Conclusion:
Docetaxel-captopril gel proved to be able to inhibit RNA expression of TGF-β1 and CTGF significantly. Captopril gel proved to be able to inhibit RNA expression of CTGF significantly. Docetaxel gel proved to be able to inhibit RNA expression of TGF-β1, CTGF, and PAI-1 significantly. There were no differences in MMP-1 expression among all study groups. Longer follow up after therapy discontinuation and greater sample size is needed to determine the therapeutic effect.
Selengkapnya:
https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/10.1177/1756287220927994

Higher level of acute serum VEGF and larger infarct volume are more frequently associated with post-stroke cognitive impairment
Astuti Prodjohardjono, Amelia Nur Vidyanti, Noor Alia Susianti, Sudarmanta, Sri Sutarni, Ismail Setyopranoto
Background
Serum vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and infarct volume detected by brain imaging have been associated with stroke outcome. However, the relationship of these two variables with post-stroke cognitive impairment (PSCI) remains unclear. We aimed to investigate the association between acute serum VEGF levels and infarct volume with PSCI in ischemic stroke patients.
Methods
Fifty-six first-ever ischemic stroke patients who were hospitalized in Dr. Sardjito General Hospital Yogyakarta, Indonesia were prospectively recruited. Serum VEGF level was taken on day 5 of stroke onset and measured by ELISA. Infarct volume was calculated manually from head CT scan by expert radiologist. PSCI was assessed after 3 months follow up by using Montreal Cognitive Assessment-Indonesian version (MoCA-INA). We performed a ROC curve analysis to determine the cut-off point of VEGF level and infarct volume. Multivariate logistic regression analysis was performed to measure the contribution of VEGF level and infarct volume to PSCI after controlling covariates (demographic and clinical data).
Results
The mean age of PSCI and non-PSCI patients was 61.63% ± 8.47 years and 58.67% ± 9.01 years, respectively (p = 0.221). No differences observed for vascular risk factors, infarct location, and NIHSS in both groups. Multivariate logistic regression showed that patients with higher VEGF level alone (≥519.8 pg/ml) were 4.99 times more likely to have PSCI than those with lower VEGF level (OR = 4.99, 95% CI = 1.01–24.7, p = 0.048). In addition, patients with larger infarct volume alone (≥0.054 ml) were also more frequently associated with PSCI (OR = 7.71, 95% CI = 1.39–42.91, p = 0.019).
Conclusions
Acute ischemic stroke patients with higher serum VEGF level (≥519.8 pg/ml) and larger infarct volume (≥0.054 ml) were more likely to have PSCI 3 months after stroke. These findings may contribute to predict PSCI earlier and thus better prevention strategy could be made.
Selengkapnya:
https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0239370

Defining a “Healthy Role-Model” for Medical Schools: Learning Components That Count
Michael Andreas Leman, Mora Claramita, Gandes Retno Rahayu
Introduction: Producing healthy physicians who act as a “healthy role-model” in their environment must be one of the concerns of medical schools today in response to the global movement of “health-promoting university” by the WHO (1995). However, no publications explained the “healthy role-model” in medical school. This study aimed to fill this gap by exploring the definition and characteristics of a “healthy role-model” for medical teachers.
Methods: We used a grounded theory approach with in-depth interviews and e-mail communications to 48 medical teachers from various backgrounds of “health professions education,” “health education and behavior”/’health education and promoter,’ “general practitioners/family medicine,” “adolescent health,” “internal medicine,” and “cardiology-vascular medicine.” The medical teachers were from Indonesia, one other developing country (Bangladesh), and five developed countries (United States of America, Canada, Netherlands, Australia, and United Kingdom). We also invited 19 medical students from Indonesia for three focus group discussions.
Results: We identified four categories to define a “healthy role-model” for medical schools as persons who are seen: 1) “physically,” “socially,” “mentally”, and “spiritually” healthy; 2) internalized healthy behaviors; 3) willing to promote healthy lifestyles; and, 4) a life-long learner. In each category, there are several characteristics discussed.
Conclusion: Our study provides some insights to define a “healthy role-model” of medical teachers by using the characteristics of healthy people and adult learners. The first category describes the characteristics of healthy people, but cultural issues influence the perspectives of medical teachers to define a “healthy role-model” for medical schools.

A protocol study of participatory action research: integrated care pathway for pregnant women with heart disease in Indonesia
Suryani Yuliyanti, Adi Utarini & Laksono Trisnantoro
Background
Heart diseases are increasingly identified as an important indirect cause of maternal mortality in several cities in Indonesia. The management of pregnancy with heart diseases requires a multidisciplinary approach, and interprofessional collaboration practice (IPCP) is critical to improving the quality of patient care. To enable the effective implementation of IPCP, integrated care pathways (ICPs) are needed to define the roles and responsibilities of the health professionals involved. This study aims to examine the obstacles and enabling factors of IPCP, to develop and use ICPs in the implementation of IPCP in health care services for pregnant women with heart diseases.
Methods
A participatory action study consisting of four stages (diagnostic, planning, implementation, and evaluation) will take approximately 2 years after consensus of ICPs are made. The primary data collection process will employ consensus, observations, focus group discussions, and in-depth interviews throughout the four stages, while secondary data from referral documents and medical records will be collected mainly during the diagnostic and evaluation stages. The findings are being analysed and will then be used to develop an ICPs through consensus building at the planning stage to be applied in the implementation stage. Finally, the implementation outcome, including acceptability, adoption, appropriateness, and feasibility of IPCP, will be assessed in the evaluation stage. All qualitative data will be analysed thematically by two coders using NVIVO 12 software.
Discussion
This research aims to assess the needs of IPCP, develop and use the ICPs in the implementation of IPCP in health care services for pregnant women with heart diseases. Findings from this study will be used for health service planning and policy making to strengthen practice of IPCP during the referral process. As a result, pregnant women with heart disease will have better access to high-quality services at every health care facility to reduce maternal mortality.
Trial registration
Retrospectively registered in the ISRCTN registry with study ID ISRCTN82300061 on Feb 6, 2019.
Selengkapnya:
https://bmchealthservres.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12913-020-05769-3

The development of Disaster Preparedness and Safety School model: A Confirmatory Factor Analysis
Evi Widowati, Wahyudi Istiono, Adi HeruHusodo.
Abstract
Educational institutions are obligated to protect children from multi-hazard disaster risks. The development of reliable and valid measuring instruments for school safety is an important component for reducing the impact of disasters on children’s future at schools. This study aimed to examine the appropriateness of measuring instrument models, constructs and indicators of the Disaster Preparedness and Safety School (SSSB) program to be used in the assessment of the multi-hazard-based child safety education system in schools. This study used an explanatory research design with a cross-sectional approach. The sampling technique used was multistage cluster sampling with 539 elementary schools as samples. The data were analyzed by Confirmatory Factor Analysis (CFA) using Lisrel 8.80 software. The CFA results showed that the SSSB constructs are considered valid and reliable. The modified model fulfilled the Goodness of Fit criteria so that the model is considered fit and suitable to be applied at schools, with school commitment as the strongest forming factor (R2 of 82%) for creating a successful SSSB program.
Selengkapnya:
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2212420920315065?via%3Dihub
