Penelitian
Pengertian
Publikasi ilmiah adalah salah satu komponen penting dalam pendidikan tinggi. Dosen dan mahasiswa khususnya di tingkat doktoral sebagai peneliti dituntut untuk memiliki publikasi di jurnal internasional sebagai salah satu hasil dari penelitian yang telah dilakukan. Tidak hanya sembarang jurnal, kita dituntut mempublikasi hasil penelitian di jurnal terindeks, termasuk di Program Studi Doktor FK-KMK UGM mensyaratkan bagi mahasiswa doktoral untuk publikasi jurnal minimum pada Quartile 3 (Q3).
Saat ini ribuan jurnal diterbitkan di seluruh dunia. Namun, tidak sedikit jurnal-jurnal predator yang menawarkan proses submisi yang mudah dan cepat namun tidak bisa dipertanggungjawabkan kualitasnya. Hal ini perlu diwaspadai agar artikel dapat dipublikasikan di jurnal terindeks dan terjamin kualitasnya.
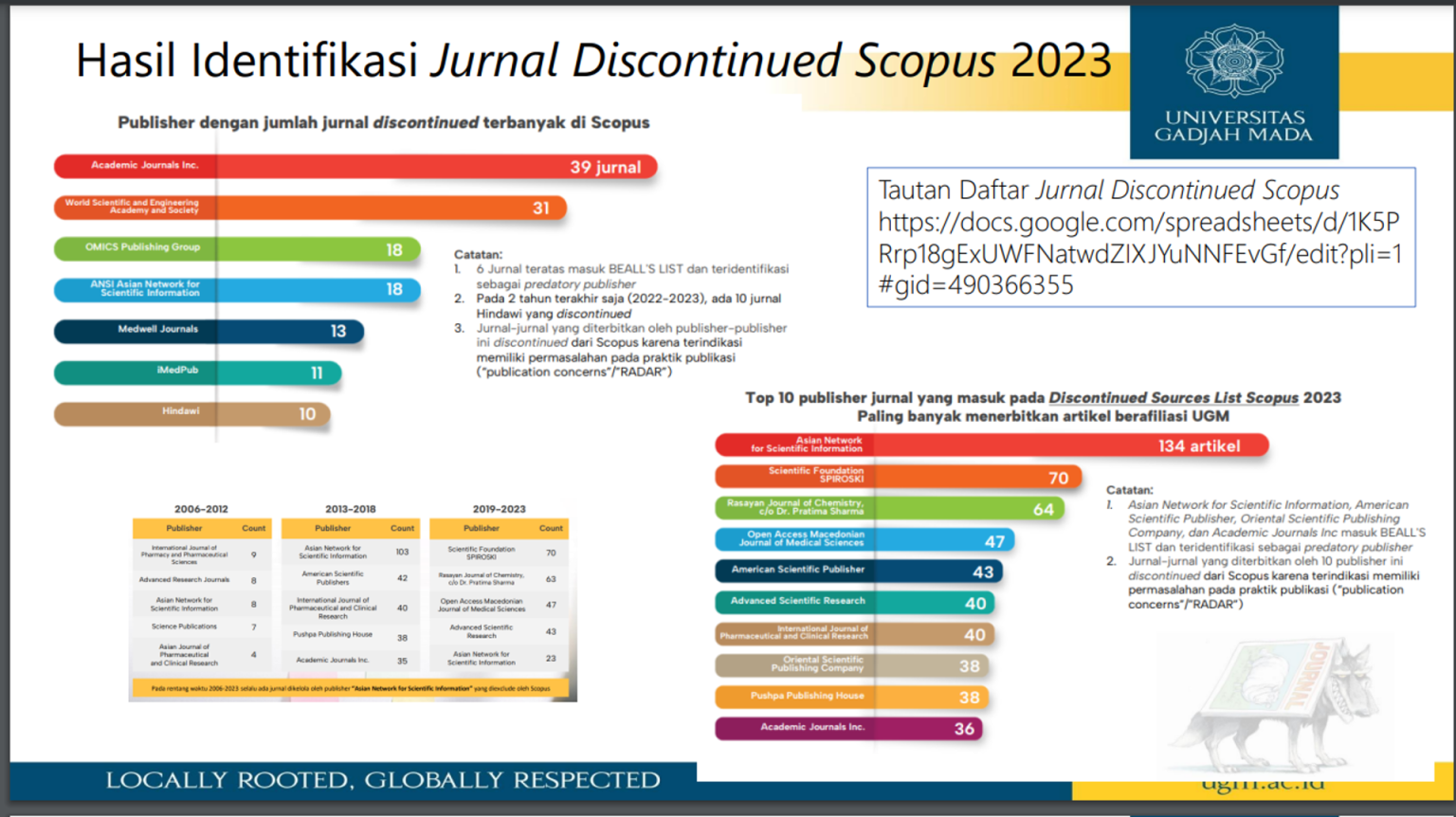
Kementerian Pendidikan dan Kebudayaan melalui Dikti telah mengidentifikasi jurnal-jurnal yang harus dihindari sebab dipertanyakan kredibilitasnya. Daftar dapat diakses melalui tautan berikut: Link
Tautan daftar lengkap Discontinued Sources List Scopus Edisi Agustus 2023: Link
Pemilihan jurnal memerlukan pertimbangan dari aspek kualitas jurnal. Bagi mahasiswa yang submit manuskrip ke jurnal yang diskontinyu Scopus setelah bulan Oktober 2023 dan manuskripnya kemudian accepted atau terpublikasi, maka manuskrip tersebut tidak dapat digunakan sebagai syarat untuk ujian tertutup.
Publikasi Mahasiswa dan Alumni Prodi Doktor FKKMK UGM

The Effect of PRKAA2 Variation on Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in the Asian Population: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Dita Maria Virginia, Iwan Dwiprahasto, Mae Sri Hartati Wahyuningsih , Dwi Aris Agung Nugrahaningsih
Abstract:
The prevalence of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) is increasing among Asians. The adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase (AMPK) increases T2DM risk through insulin resistance. Glucose levels are related to AMPK subunit α2 encoded by PRKAA2. This systematic review and meta-analysis aimed to analyse the association between PRKAA2 variation and T2DM risk. Publication search related to PRKAA2 and T2DM used PubMed, ProQuest, and ScienceDirect databases. Article selection based on inclusion and exclusion criteria only included Japanese and Chinese populations. This meta-analysis used five genotype models to estimate the effect of PRKAA2 variation and T2DM risk. Additionally, a fixed-effect model was selected to measure the pooled size effect if P > 0.05 or I2 < 50%. Qualitative analysis included four eligible studies, and meta-analysis included only two studies because both showed data concerning rs2746342 variation. Patients with G allele are 1.45 times more likely to have T2DM than patients with T allele (95% confidence interval [CI]: 1.20, 1.76; P: 0.0001). Notably, patients who had GG genotype have 1.96 times higher risk of T2DM compared with those with TT genotype (95% CI: 1.34, 2.87; P: 0.0005), dominant model (odds ratio [OR]: 1.75; 95% CI: 1.32, 2.31; P: 0.001), and recessive model (OR: 1.43; 95% CI: 1.01, 2.01; P: 0.04). PRKAA2 variation, especially in rs2746342, has an association with T2DM risk in the G allele, additive, dominant, and recessive models. G allele might be the most contributable factor in increasing T2DM susceptibility.
Keywords: AMP-activated protein kinase, genetic variation, type 2 diabetes mellitus, risk factor, Asian

The difference in collagen type-1 expression in women with and without pelvic organ prolapse: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Pelvic organ prolapse (POP) adalah organ dasar panggul yang turun dari tempat seharusnya. Kondisi ini terjadi akibat otot dan ligamen yang menyokong organ-organ di sekitar daerah panggul melemah. Kondisi ini merupakan gangguan umum di kasus ginekologi, dengan sekitar 37% pasien melakukan pengobatan medis. Meskipun POP tidak menyebabkan kematian atau keparahan penyakit yang signifikan, POP dapat menyebabkan penurunan kualitas hidup wanita.
Beberapa faktor risiko yang terkait dengan POP telah diidentifikasi dan dipelajari, termasuk usia, paritas, status menopause, indeks massa tubuh, ras, genetika, gangguan jaringan ikat, merokok, peningkatan tekanan perut kronis seperti pekerjaan fisik atau penyakit paru-paru kronis, sembelit kronis, dan riwayat operasi sebelumnya.
Secara molekuler, perubahan matriks ekstraseluler (ECM) pada jaringan ikat struktur dasar panggul termasuk ligamen sakrouterina, ligamen kardinal, dan fasia endopelvis dapat berkontribusi pada kejadian prolaps organ panggul (POP).
Berkurangnya kandungan kolagen, perubahan rasio jenis kolagen dan perubahan kolagen dikaitkan (cross-linking) pada sistem pendukung dasar panggul, termasuk ligamen sakrouterina, ligamen kardinal, dan fasia endopelvis pada wanita dengan POP. Namun berbagai penelitian masih menunjukkan hasil dan data yang dapat diberdebatkan karena minimnya ukuran sampel, lokasi biopsi dan metodenya.
Selengkapnya di: bit.ly/Paper-Akbar

Roles and Problems of Stroke Caregivers: A Qualitative Study in Yogyakarta, Indonesia
Caregiver memainkan peran utama dalam perawatan pasien pasca stroke. Sejumlah besar perawatan, terutama untuk melakukan aktivitas hidup sehari-hari, sangat penting bagi penderita stroke untuk meningkatkan status fungsional mereka. Oleh karena itu, caregiver disarankan untuk terlibat dalam perawatan pasien pasca stroke untuk meningkatkan kualitas manajemen pasien. Saat ini, terdapat banyak penelitian terkait pengalaman merawat pasien pasca stroke. Namun, peran dan masalah yang dikelola oleh caregiver saat merawat pasien pasca stroke di Indonesia belum banyak diteliti. Oleh karena itu, penelitian ini bertujuan untuk mengeksplorasi peran dan masalah caregiver pasca stroke di Indonesia.
Selengkapnya: bit.ly/Paper-Paryono

Density of tobacco advertising around schools
Nurjanah, N., Manglapy, Y. M., Handayani, S., Ahsan, A., Sutomo, R., Dewi, F. S. T., Chang, P., Kusuma, D.
Abstract
BACKGROUND: Indonesia has the second highest smoking prevalence among adult males in the world, with over 61.4 million current smokers. However, there is no national regulation on outdoor tobacco advertising.
OBJECTIVE: >To assess the density of outdoor tobacco advertising around schools in Semarang City, Indonesia.
METHODS: We conducted geospatial analyses using buffer and hotspot analyses based on advertising and school data in ArcMap 10.6. We statistically tested the significance of different densities, including between 100 m and 100–300-m buffers from schools using Stata 15.1.
RESULTS: We found a total of 3453 tobacco advertisements, of which 3026 (87%) were at least medium in size (1.3 m x l.9 m), and 2556 (74%) were within 300 m of schools. We also found hotspots with a 45% higher density of adverts within 100 m of schools (compared to within 100–300 m). A total of 378 schools (39%) were in these advertising hotspots.
CONCLUSION: There was high density of outdoor tobacco advertising, with significant clusters in close proximity to schools in Semarang City. The policy implications of this are discussed.
[wpdm_package id=’3685′]

Piper crocatum Ruiz & Pav. ameliorates wound healing through p53, E-cadherin and SOD1 pathways on wounded hyperglycemia fibroblasts
Andina Setyawati, Mae Sri Hartati Wahyuningsih, Dwi Aris Agung Nugrahaningsih, Christanti Effendy, Firas Fneish, Gerhard Fortwengel
Introduction
Piper crocatum Ruiz & Pav (P. crocatum) has been reported to accelerate the diabetic wound healing process empirically. Some studies showed the benefits of P. crocatum in treating various diseases but its mechanisms in diabetic wound healing have never been reported. In the present study we investigated the diabetic wound healing activity of the active fraction of P. crocatum on wounded hyperglycemia fibroblasts (wHFs).
Methods
Bioassay-guided fractionation was performed to get the most active fraction. The selected active fraction was applied to wHFs within 72 h incubation. Mimicking a diabetic condition was done using basal glucose media containing an additional 17 mMol/L D-glucose. A wound was simulated via the scratch assay. The collagen deposition was measured using Picro-Sirius Red and wound closure was measured using scratch wound assay. Underlying mechanisms through p53, αSMA, SOD1 and E-cadherin were measured using western blotting.
Results
We reported that FIV is the most active fraction of P. crocatum. We confirmed that FIV\(7.81 µg/ml, 15.62 µg/ml, 31.25 µg/ml, 62.5 µg/ml, and 125 µg/ml) induced the collagen deposition and wound closure of wHFs. Furthermore, FIV treatment (7.81 µg/ml, 15.62 µg/ml, 31.25 µg/ml) down-regulated the protein expression level of p53 and up-regulated the protein expression levels of αSMA, E-cadherin, and SOD1.
Discussion/conclusions
Our findings suggest that ameliorating collagen deposition and wound closure through protein regulation of p53, αSMA, E-cadherin, and SOD1 are some of the mechanisms by which FIV of P. crocatum is involved in diabetic wound healing therapy.
Selengkapnya:
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1319562X21007245

Hospitals accreditation status in Indonesia: associated with hospital characteristics, market competition intensity, and hospital performance?
Viera Wardhani, Jitse Pieter van Dijk & Adi Utarini
Background
Hospital accreditation is widely adopted as a visible measure of an organisation’s quality and safety management standards compliance. There is still inconsistent evidence regarding the influence of hospital accreditation on hospital performance, with limited studies in developing countries. This study aims to explore the association of hospital characteristics and market competition with hospital accreditation status and to investigate whether accreditation status differentiate hospital performance.
Methods
East Java Province, with a total 346 hospitals was selected for this study. Hospital characteristics (size, specialty, ownership) and performance indicator (bed occupancy rate, turnover interval, average length of stay, gross mortality rate, and net mortality rate) were retrieved from national hospital database while hospital accreditation status were recorded based on hospital accreditation report. Market density, Herfindahl-Hirschman index (HHI), and hospitals relative size as competition indicators were calculated based on the provincial statistical report data. Logistic regression, Mann-Whitney U-test, and one sample t-test were used to analyse the data.
Results
A total of 217 (62.7%) hospitals were accredited. Hospital size and ownership were significantly associated with of accreditation status. When compared to government-owned, hospital managed by ministry of defense (B = 1.705, p = 0.012) has higher probability to be accredited. Though not statistically significant, accredited hospitals had higher utility and efficiency indicators, as well as higher mortality.
Conclusions
Hospital with higher size and managed by government have higher probability to be accredited independent to its specialty and the intensity of market competition. Higher utility and mortality in accredited hospitals needs further investigation.
Selengkapnya:
https://bmchealthservres.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12913-019-4187-x
