Penelitian
Pengertian
Publikasi ilmiah adalah salah satu komponen penting dalam pendidikan tinggi. Dosen dan mahasiswa khususnya di tingkat doktoral sebagai peneliti dituntut untuk memiliki publikasi di jurnal internasional sebagai salah satu hasil dari penelitian yang telah dilakukan. Tidak hanya sembarang jurnal, kita dituntut mempublikasi hasil penelitian di jurnal terindeks, termasuk di Program Studi Doktor FK-KMK UGM mensyaratkan bagi mahasiswa doktoral untuk publikasi jurnal minimum pada Quartile 3 (Q3).
Saat ini ribuan jurnal diterbitkan di seluruh dunia. Namun, tidak sedikit jurnal-jurnal predator yang menawarkan proses submisi yang mudah dan cepat namun tidak bisa dipertanggungjawabkan kualitasnya. Hal ini perlu diwaspadai agar artikel dapat dipublikasikan di jurnal terindeks dan terjamin kualitasnya.
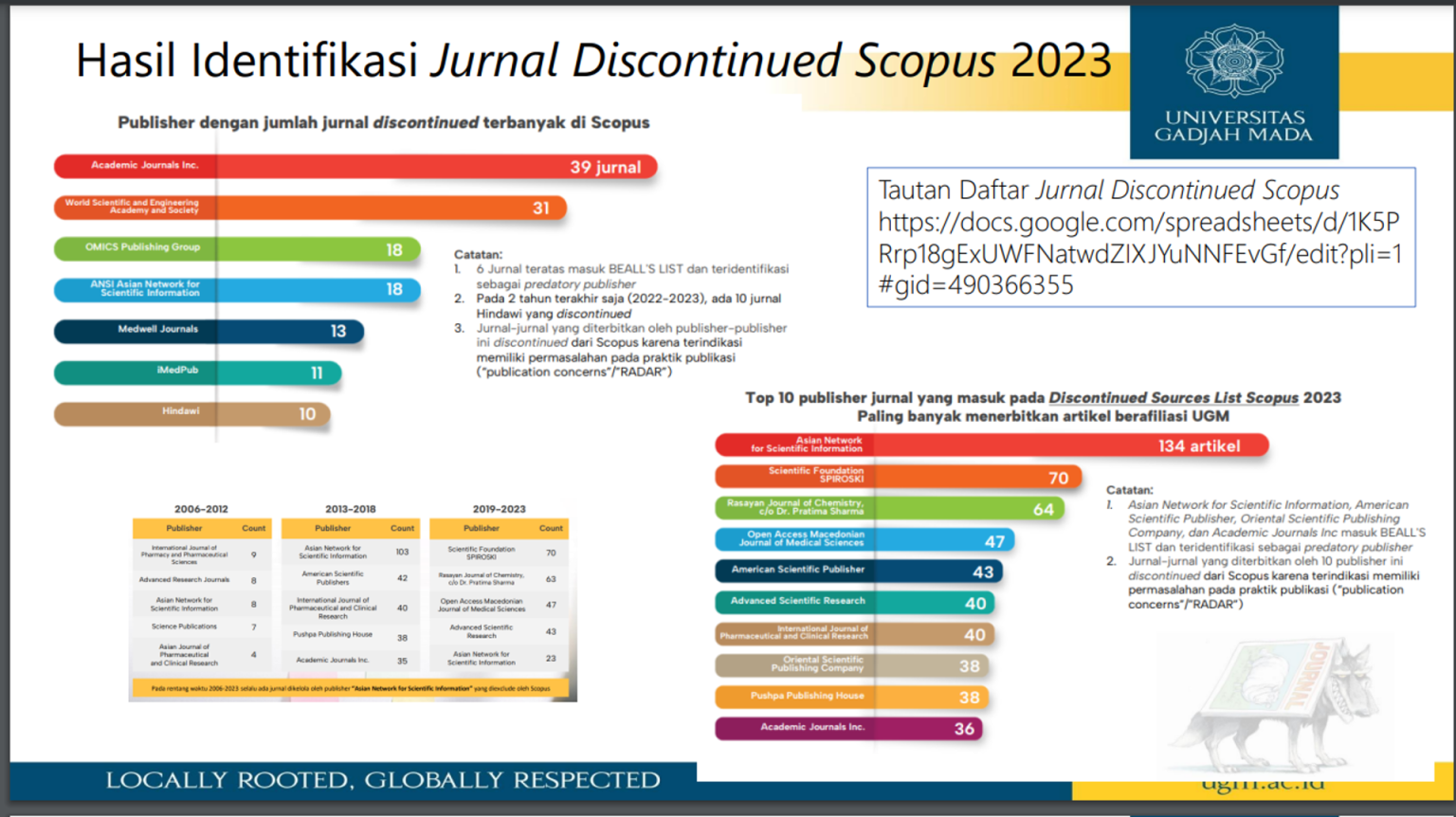
Kementerian Pendidikan dan Kebudayaan melalui Dikti telah mengidentifikasi jurnal-jurnal yang harus dihindari sebab dipertanyakan kredibilitasnya. Daftar dapat diakses melalui tautan berikut: Link
Tautan daftar lengkap Discontinued Sources List Scopus Edisi Agustus 2023: Link
Pemilihan jurnal memerlukan pertimbangan dari aspek kualitas jurnal. Bagi mahasiswa yang submit manuskrip ke jurnal yang diskontinyu Scopus setelah bulan Oktober 2023 dan manuskripnya kemudian accepted atau terpublikasi, maka manuskrip tersebut tidak dapat digunakan sebagai syarat untuk ujian tertutup.
Publikasi Mahasiswa dan Alumni Prodi Doktor FKKMK UGM

Secular trends in Javanese adult height: the roles of environment and educational attainment
The interactional communication of feedback in clinical education: A focused ethnographic study in a hierarchical and collectivist culture

Screening antibiofilm activity of invasive plants growing at the Slope Merapi Mountain, Central Java, against Candida albicans
Abstract
Background Candida albicans causes high-mortality candidiasis. Antifungal drug resistance demands the devel- opment of virulence factor-targeting drugs, particularly antibiofilm. This study screened the effects of five invasive plants growing in Indonesia (Mimosa pudica, Lantana camara, Acacia mangium, Ageratina riparia, and Mikania micran- tha) against C. albicans biofilms. Antifungal activity, antiphospholipase activity, biofilm morphology of C. albicans, and cytotoxic capacity were also evaluated.
Methods Maceration was used to extract the plants, and the most active extract inhibiting the biofilms was fraction- ated using liquid–liquid fractionation. Antibiofilm activity was determined by a colorimetric assay, MTT. Antifungal activity was tested using the broth microdilution method. A phospholipase assay was performed using the egg-yolk agar method. Influence on the C. albicans morphology was assessed using scanning electron microscopy (SEM).
The cytotoxic effect was carried out against Vero and HeLa cell lines.
Results M. pudica extracts showed the most potent antifungal efficacy with minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) of 15.62 µg/mL and 7.81 µg/mL for aerial parts and roots, respectively. At high concentrations (500 µg/mL and 250 µg/mL), ethanol extract of M. pudica aerial parts strongly inhibited the phospholipase activity. Ethyl-acetate fraction of M. pudica aerial parts demonstrated the most potent antibiofilm activity against 24 h old biofilm of C. albicans with an inhibitory concentration (53.89%) of 62.5 µg/mL showed no cytotoxicity in both Vero and HeLa cells. This fraction affected the morphology of C. albicans and contained promising compounds for inhibiting the 24 h old biofilm of C. albicans.
Conclusions Invasive M. pudica plant inhibited the growth of planktonic C. albicans cells and its ethyl acetate fraction decreased the metabolic activity of C. albicans biofilms. This result demonstrates the potential of invasive M. pudica plant to reduce biofilm-associated candida infection.
Keywords Invasive plants, Candida albicans, Antifungal, Antibiofilm, Mimosa pudica

Outcomes of vaccinations against respiratory diseases in patients with end-stage renal disease undergoing hemodialysis: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Metalia Puspitasari ,Prenali D. Sattwika ,Dzerlina S. Rahari ,Wynne Wijaya ,Auliana R. P. Hidayat ,Nyoman Kertia ,Bambang Purwanto ,Jarir At Thobari
Abstract
Due to the nature of the disease, end-stage renal disease (ESRD) patients suffer from dysfunction of the adaptive immune system, which leads to a poorer response to vaccination. Accordingly, it is crucial to evaluate the efficacy and safety of management strategies, including vaccinations, which could potentially reduce the risk of respiratory diseases, such as pneumonia, influenza, or COVID-19, and its associated outcomes. We searched PubMed, CENTRAL, ScienceDirect, Scopus, ProQuest, and Google Scholar databases using designated MeSH keywords. The risk of bias was assessed using ROBINS-I. The quality of evidence was assessed using the GRADE (Grading of Recommendations, Assessment, Development, and Evaluation) approach. Relative risk (RR) and 95% confidence interval (CI) were calculated. Heterogeneity was investigated using forest plots and I2 statistics. This systematic review included a total of 48 studies, with 13 studies of influenza (H1N1 and H3N2) vaccination and 35 studies of COVID-19 vaccination. H1N1 vaccination in ESRD patients undergoing hemodialysis induced lower seroconversion rates (RR 0.62, 95% CI: 0.56–0.68, p <0.00001) and lower seroprotection rates (RR 0.76, 95% CI: 0.70–0.83, p <0.00001) compared to controls. H3N2 vaccination in ESRD patients undergoing hemodialysis yielded lower seroconversion rates (RR 0.76, 95% CI: 0.68–0.85, p <0.00001) and lower seroprotection rates (RR 0.84, 95% CI: 0.77–0.90, p <0.00001) compared to controls. Twenty-nine studies demonstrate significantly lower antibody levels in ESRD patients undergoing hemodialysis compared to the controls following COVID-19 vaccination. This review presents evidence of lower seroconversion and seroprotection rates after vaccination against viral respiratory diseases in patients with ESRD undergoing hemodialysis. Since hemodialysis patients are more susceptible to infection and severe disease progression, a weakened yet substantial serological response can be considered adequate to recommend vaccination against respiratory diseases in this population. Vaccination dose, schedule, or strategy adjustments should be considered in stable ESRD patients on maintenance hemodialysis.

Integrated Diabetes Self-Management (IDSM) mobile application to improve selfmanagement and glycemic control among patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (T2DM) in Indonesia: A mixed methods study protocol
𝗜𝗻𝘁𝗲𝗴𝗿𝗮𝘁𝗲𝗱 𝗗𝗶𝗮𝗯𝗲𝘁𝗲𝘀 𝗦𝗲𝗹𝗳 𝗠𝗮𝗻𝗮𝗴𝗲𝗺𝗲𝗻𝘁 (𝗜𝗗𝗦𝗠) 𝗺𝗼𝗯𝗶𝗹𝗲 𝗮𝗽𝗽𝗹𝗶𝗰𝗮𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻 𝘁𝗼 𝗶𝗺𝗽𝗿𝗼𝘃𝗲 𝘀𝗲𝗹𝗳𝗺𝗮𝗻𝗮𝗴𝗲𝗺𝗲𝗻𝘁 𝗮𝗻𝗱 𝗴𝗹𝘆𝗰𝗲𝗺𝗶𝗰 𝗰𝗼𝗻𝘁𝗿𝗼𝗹 𝗮𝗺𝗼𝗻𝗴 𝗽𝗮𝘁𝗶𝗲𝗻𝘁𝘀 𝘄𝗶𝘁𝗵 𝗧𝘆𝗽𝗲 𝟮 𝗗𝗶𝗮𝗯𝗲𝘁𝗲𝘀 𝗠𝗲𝗹𝗹𝗶𝘁𝘂𝘀 (𝗧𝟮𝗗𝗠) 𝗶𝗻 𝗜𝗻𝗱𝗼𝗻𝗲𝘀𝗶𝗮: 𝗔 𝗺𝗶𝘅𝗲𝗱 𝗺𝗲𝘁𝗵𝗼𝗱𝘀 𝘀𝘁𝘂𝗱𝘆 𝗽𝗿𝗼𝘁𝗼𝗰𝗼𝗹
oleh
Dewi Murdiyanti Prihatin Putri, Yoyo Suhoyo, Ariani Arista Putri Pertiwi, Christantie Effendy
Penelitian ini memiliki tujuan menginisiasi teknologi aplikasi berbasis android sebagai alat bagi pasien, keluarga, dan penyedia layanan kesehatan untuk mengoptimalkan pengobatan diabetes melitus tipe 2. Desain studi exploratory sequential mixed-methods digunakan dalam penelitian dengan tiga tahap. Tahap pertama akan menggunakan metode deskriptif kualitatif. Pasien, keluarga, perawat, dokter, dan petugas BPJS akan dilibatkan dalam FGD dan wawancara. Selanjutnya, tahap kedua akan dilakukan pengembangan aplikasi android berdasarkan hasil pada tahap pertama. Pada tahap ketiga, umpan balik dari pengguna akan dikumpulkan setelah menggunakan aplikasi selama tiga bulan. Hasil dari penelitian direncanakan berupa aplikasi yang bernama Integrated Diabetes Self-Management (IDSM).
Buku panduan bagi penderita diabetes melitus yang berjudul “Sehat dengan DiaRIn: Diabetes Melitus Terintegrasi di Indonesia” merupakan luaran dari penelitian ini.

